What Is SaaS (Software as a Service)?

5 min read
Table of Contents
Software as a Service, also called SaaS, is a modern way to use software through the internet. Instead of installing programs on local computers, users access software through an internet browser. This method removes many technical barriers that businesses once faced.
When people ask what SaaS is, the answer is simple. SaaS delivers software applications using cloud computing. The software runs on a secure cloud infrastructure managed by a cloud service provider. Users only need internet access to begin using the service.
Unlike traditional software, SaaS software does not require installing software on individual devices. Businesses no longer manage operating systems, servers, or updates. The SaaS vendor handles software maintenance, security patches, and infrastructure management. This approach saves time, lowers costs, and reduces technical effort.
Many SaaS companies now support daily business operations worldwide. From customer relationship management to project management, SaaS applications help teams work faster and smarter. SaaS supports remote teams, mobile users, and growing businesses with ease.
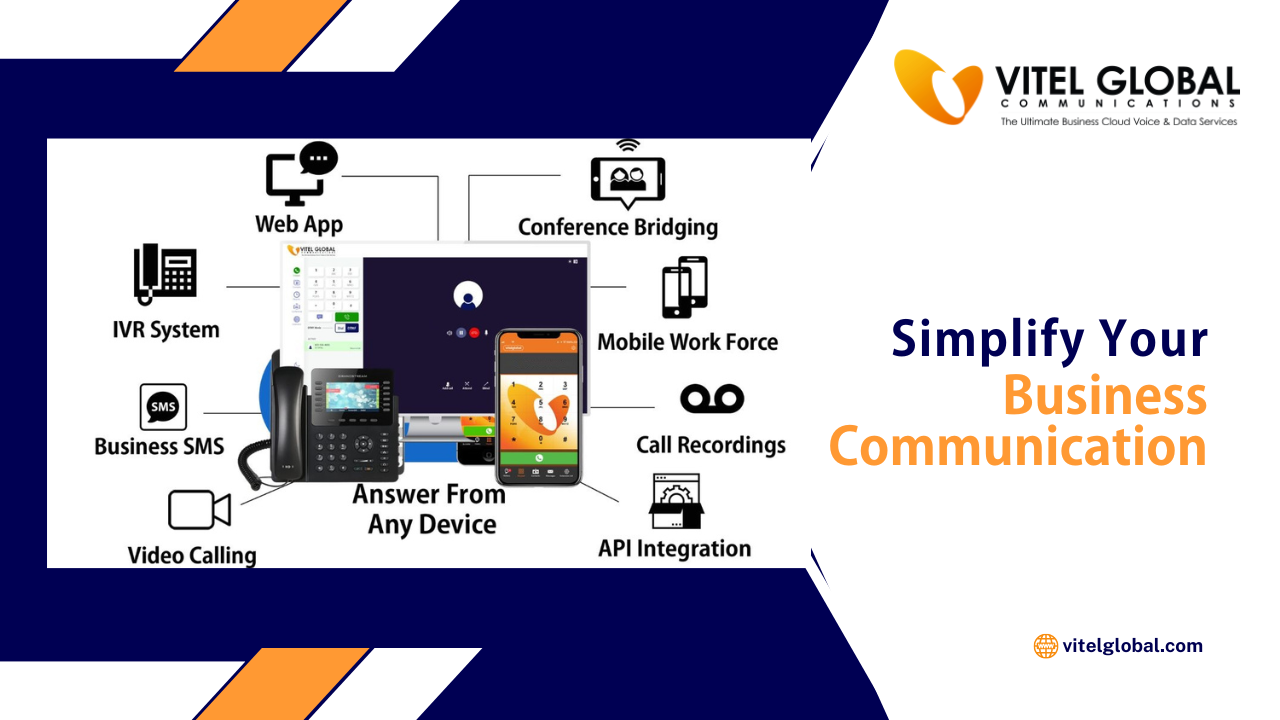
Vitel Global uses the SaaS business model to deliver cloud-based communication solutions. Businesses use calling, messaging, and analytics as SaaS offerings without hardware. This cloud delivery model improves flexibility, reliability, and long-term business value.
Key Takeaways
- Software as a Service uses cloud-based applications
- SaaS applications run through internet access
- SaaS providers manage updates and data security
- Users pay recurring fees instead of buying licenses
- SaaS supports rapid deployment and business growth
What Does Software as a Service Mean?
Software as a Service means software hosted by a cloud provider rather than installed on on-premises software systems. Users access SaaS applications online using secure login credentials. The service provider owns and manages the software resources.
In SaaS defined software, the same application supports multiple users. This structure is called multiple tenancies. Each customer uses the same software instance, but customer data stays isolated and protected.
This SaaS model reduces technical responsibility for SaaS customers. Businesses do not manage servers, data centers, or infrastructure. The SaaS vendor handles software updates, data storage, and system reliability.
How Does SaaS Work?
To understand how SaaS works, it helps to look at cloud services. SaaS applications run inside professional data centers operated by cloud service providers. These data centers ensure uptime, backups, and monitoring.
Users connect to SaaS apps through an internet browser or mobile device. User access is controlled using login systems and permissions. Only authorized users can reach sensitive information.
Most SaaS providers use a single instance architecture. This single instance supports multiple customers securely. This cloud delivery model lowers costs while maintaining performance and data security.
SaaS Versus Traditional Software
Traditional software installs directly on local computers. Businesses manage licenses, updates, and infrastructure management. Fixing issues often requires technical teams.
Unlike traditional software, SaaS software removes these steps. There is no installation process. Automatic updates run in the background without user action.
SaaS enables faster deployment. Teams begin using software applications within hours. This speed helps businesses adapt quickly to changing needs.
Core Features of SaaS Platforms
Modern SaaS applications share several important features. They support multiple users through structured access management. Admins control permissions easily.
SaaS apps work across devices. Desktop users, mobile users, and remote teams access the same system. Internet access is the only requirement.
Automatic updates keep software secure and current. Security patches are applied regularly. This improves enhanced security compared to local systems.
Common SaaS Applications in Business
SaaS applications support many business functions today. Customer relationship management tools help sales teams track leads and interactions. Enterprise resource planning systems manage finance and operations.
Human resources teams use SaaS for hiring, payroll, and records. Project management tools support collaboration and planning.
Vitel Global provides SaaS solutions for communication. Businesses manage calls, messages, and customer data through one cloud-based platform.
SaaS Pricing Models Explained
Most SaaS companies use subscription pricing. Users pay recurring fees monthly or annually. This covers cloud infrastructure, updates, and support.
Some SaaS vendors offer tiered pricing. Each tier includes different features and usage limits. Businesses select plans that match their needs.
Usage-based pricing is also common. Costs grow with activity, making billing fair and predictable.
Benefits of SaaS for Businesses
SaaS advantages are clear across industries. Businesses avoid high upfront costs by skipping hardware purchases. Infrastructure as a service is included.
Automatic updates reduce downtime. Users always access modern SaaS applications without manual effort.
Scalability improves growth. SaaS users add accounts quickly without system changes.
SaaS Security and Data Protection
Data security is a priority for SaaS providers. Encryption protects customer data during storage and transfer. Access management limits exposure.
Only authorized users can access systems. Activity logs support monitoring and compliance.
Most SaaS providers apply stronger protections than internal systems. Zero-trust security models add further safety.
SaaS Integration With Business Systems
SaaS platforms integrate with other business applications. Companies connect CRM, ERP, and communication tools.
These integrations reduce manual work. Data flows smoothly across systems. This improves efficiency and accuracy.
Vitel Global integrates SaaS communication tools with business systems to support smooth workflows.
SaaS Ownership and Vendor Responsibility
In SaaS, businesses own their customer data. The SaaS vendor manages software delivery and cloud infrastructure.
Service providers handle uptime, updates, and infrastructure management. Customers control user access and policies.
Clear agreements define responsibilities and build trust.
SaaS and Cloud Computing Relationship
SaaS is part of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a Service provides servers and storage. Platform services support application development.
SaaS delivers complete software applications. Users do not manage infrastructure.
This makes SaaS the easiest cloud model to adopt.
SaaS for Remote and Mobile Teams
SaaS supports remote work naturally. Employees access tools from any location.
Mobile users work from phones, tablets, or laptops. Cloud-based applications support flexibility.
This model fits modern work environments.
SaaS Tools Offered by Vitel Global
Vitel Global delivers SaaS-based communication platforms. Businesses manage calls, messages, and analytics from one dashboard.
The system scales easily. No hardware installation is required.
Cloud delivery ensures reliable performance across regions.
SaaS and Business Growth
SaaS supports long-term growth. Businesses add users without system upgrades.
New features appear automatically. SaaS development continues without disruption.
Integrations support efficiency and adaptability.
Challenges When Using SaaS
Some businesses worry about internet dependence. Others worry about data control.
Choosing reliable SaaS providers reduces risks. Strong access controls protect data.
Training helps teams adopt SaaS tools quickly.
SaaS in Digital Transformation
Digital transformation depends on SaaS. Businesses replace legacy systems with cloud-based applications.
SaaS supports emerging technologies and automation. Organizations adapt faster.
SaaS Use Cases Across Industries
Retail uses SaaS for inventory.
Healthcare uses SaaS for secure communication.
Education platforms support online learning.
SaaS adapts across industries.
SaaS Deployment Speed and Efficiency
SaaS enables rapid deployment. No physical setup is required.
Users receive access quickly. Teams start working immediately.
This improves productivity and reduces delays.
Conclusion
Software as a Service has transformed how businesses use software applications. The SaaS model removes installation barriers and reduces technical effort.
By using cloud computing and cloud services, SaaS delivers flexibility, scalability, and security. Businesses gain faster deployment and lower costs.
Vitel Global delivers communication solutions using the SaaS business model. With cloud-based platforms, businesses stay connected, secure, and ready for long-term growth.
Simplify Operations With Scalable SaaS Solutions
Adopt cloud-based SaaS solutions to reduce complexity, improve flexibility, and support secure business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions About SaaS
1. What is Software as a Service?
Software as a Service is a cloud delivery model where users access software through the internet. SaaS providers manage hosting, software maintenance, data storage, and security, allowing businesses to focus on daily operations instead of infrastructure management.
2. How does SaaS differ from traditional software?
Traditional software installs on local computers and requires manual updates. SaaS software runs through cloud services, offers automatic updates, stronger data security, easier access management, and lower infrastructure responsibilities for businesses.
3. Who typically uses SaaS applications?
SaaS users include startups, enterprises, and mobile users. Teams across customer relationship management, human resources, project management, and data management rely on SaaS applications every day.
4. Is SaaS secure for business use?
Most SaaS providers apply encryption, access controls, and zero-trust security models. Regular security patches and monitoring protect customer data across multiple customers and tenants.
5. Why do SaaS platforms use subscription pricing?
Subscription pricing covers cloud infrastructure, software resources, updates, and support. This model ensures predictable costs while allowing continuous improvements and scalable access.
Published: December 26th, 2025
Subscribe to Our Latest Updates
Get monthly product and feature updates, the latest industry news, and more!